
Eye Colour
The genes that control melanin production that alter the expression of coat colour and pigment can also affect eye colour.
The pigmentation of the iris of the eye varies depending on the content of melanin, among other things. Havanese that have black pigment have brown eyes from medium brown to dark brown to almost black. Different colour eyes in Havanese occur when the melanin expression is affected by other genes such as the brown gene or dilution gene. The gene mutation that causes brown to be formed instead of black also affects the eye colour. Because of this, the eyes of chocolate Havanese range from brown hazel to light or medium brown. The darker shades of brown eyes of the chocolate Havanese can overlap the lighter shades occasionally seen in black pigmented dogs. The dilution gene also affects eye colour. Dilute black (blue) dogs will have a diluted eye colour which can be clear to dull blue, grey hazel, or grey. Dilute chocolate dogs will have eyes that are golden hazel, grey green, or yellow amber.
Dark brown Medium brown Light brown(chocolate) Golden brown

Light Golden Brown Dilute(blue) Dilute (gray/green) Dilute (yellow/amber)


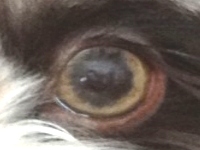
Blue Eyes
Dilution (above) is not the only reason a Havanese can have blue eyes. There are at least three possibilities with many clues to tell them apart.
1) The first and most common reason for blue eyes is puppyhood. Regardless of the coat colour, the eyes of very young puppies are generally medium to dark blue when they first open. The eyes do not stay blue; they gradually settle to their true colours within the next eight to ten weeks. See progression below.
2) The blue eyes of the dilute Havanese (as shown above) will be paired with a dilute coat colour and dilute pigment. This is easy to tell in an adult dog.
3) To the right is an example of something unusual, a bi-eyed dog with one brown eye and one china blue eye. Heterochromia, a difference in coloration, is a result of unequal distribution of melanin in a particular localized area such as the eye. The colour difference can be due to hyperpigmentation (too much pigment) or hypopigmentation (too little pigment). The phenomenon is found in other dog breeds, the most commonly known being the Husky. Although a colour difference can be acquired by trauma or infection, for the most part it is inherited. In the case of this Hungarian born Havanese, it is definitley inherited as a half-sibling is also bi-eyed, while another half-sibling has two blue eyes. This blue eye colour is not related to either puppyhood or to colour dilution. You can see that the other eye is deep brown as expected and the nose pigment is black.
PUPPY EYE DEVELOPMENT
Regardless of body coat colour, when the eyes open at 10-14 days, young puppies generally all have blue eyes. The colour of the eyes develops over the next 8-10 weeks. Watch this chocolate puppy's eyes change from deep blue to golden over the span of a few weeks.
Three weeks 4 weeks 6 weeks 8 weeks




NEXT ... definitions of pad & nail colour